Open Sourcing Farm Card Calculations
Overview
- Project Background
- What are ‘farm cards’?
- Setting Up
- Getting Data
- Processing
- Questions?
Background
What We Had
- Proprietary
- Expensive
- Dependent upon 2 additional proprietary softwares (ArcMap and MS Access)
- Used deprecated file types
- Time consuming
- Inaccurate!
What I Wanted
- Accurate
- Simple
- Fast
- Accessible
What are Farm Cards?
TLDR
It’s how we generate property values for agricultural parcels. Values are derived from a parcel’s slope, soil type, and land use.
Full details can be found in the Illinois Department of Revenue’s Publication 122.
Individual Soil Weighting Method
There is a 10-step process given for how these calculations are done. Our primary focus has been step four:
Determine the acreage of each soil type within each land use category that will be assessed by productivity.
In other words, a spatial overlay.
Set up the Environment
Modules
Globals
sr = "{'wkid': 3435}"
parcels_url = 'https://maps.co.kendall.il.us/server/rest/services/Hosted/Current_Cadastral_Features/FeatureServer/1/query?'
soils_url = 'https://maps.co.kendall.il.us/server/rest/services/Hosted/Assessor_Soils/FeatureServer/0/query?'
landuse_url = 'https://maps.co.kendall.il.us/server/rest/services/Hosted/Assessor_Landuse/FeatureServer/0/query?'
out_dir = os.path.expanduser('~/')
export_name = f"farms_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M')}"
file = os.path.join(out_dir, f'{export_name}.txt')Getting Data: Parcels
parcels_params = {
'where': "pin_dashless LIKE '0827%' and class IN ('0011', '0021')",
'outFields': 'gross_acres, pin',
'outSR': sr,
'f': 'geojson'
}
parcels = requests.get(parcels_url, parcels_params)
p_df = gp.read_file(parcels.text)
p_df.sample()| pin | gross_acres | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 08-27-400-008 | 158.85 | POLYGON ((964473.520 1753276.450, 964473.180 1... |
Other Data Sources?
GeoPandas can handle pretty much anything, thanks to the Fiona module.
- Shapefiles (zipped and unzipped)
- File Geodatabases
- GeoPackages
- GeoJSON
- PostGIS
- Other spatial database tables (with some help from Pandas)
Getting Data: Soil and Landuse
Create a Spatial Filter
We’ll use the bounding box of our parcels to query any features that intersect with the parcels.
farm_params = {
'where': '1=1',
'outFields': '*',
'returnGeometry': True,
'geometryType': 'esriGeometryEnvelope',
'geometry': bbox,
'spatialRel': 'esriSpatialRelIntersects',
'outSR': sr,
'f': 'geojson'
}
soils = requests.get(soils_url, farm_params)
s_df = gp.read_file(soils.text)
s_df.loc[:, 'slope'].fillna('', inplace=True)
landuse = requests.get(landuse_url, farm_params)
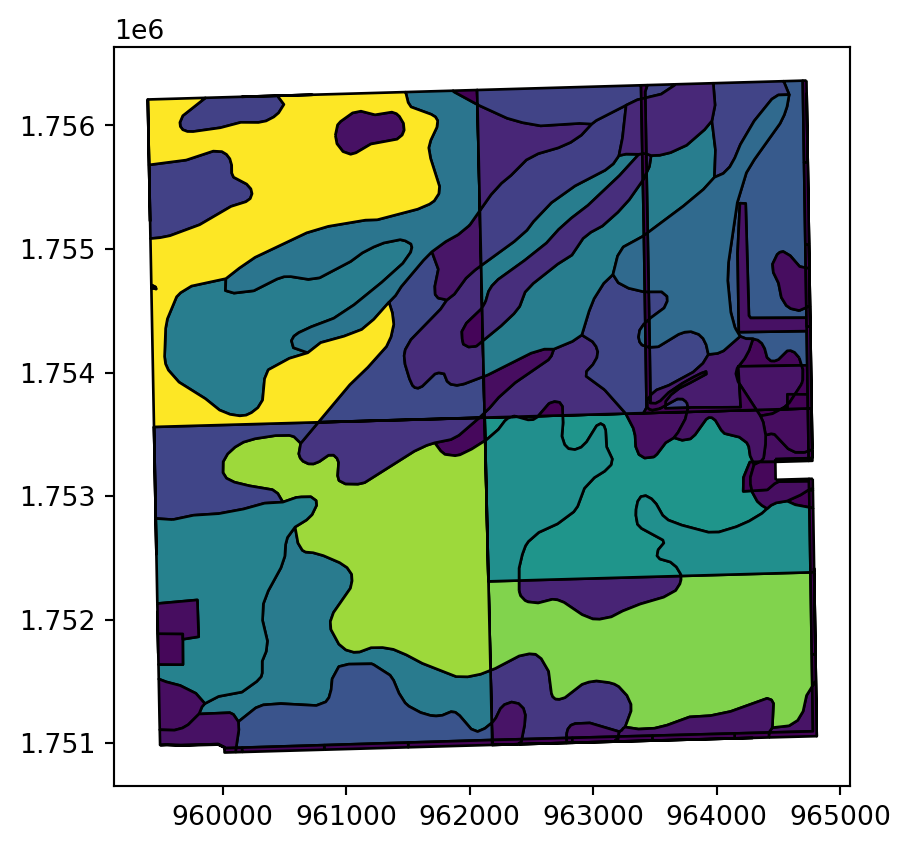
l_df = gp.read_file(landuse.text)Visualize Layers
Calculated Area
Deeded acres ≠ Measured acres
We need a ratio
\[ \frac{DeedAc_{part}}{DeedAc_{whole}} = \frac{MeasFt^{2}_{part}}{MeasFt^{2}_{whole}} \\ \big\downarrow \\ DeedAc_{part} = DeedAc_{whole} * \frac{MeasFt^{2}_{part}}{MeasFt^{2}_{whole}} \]
Add Area to Parcels
Data Manipulation
Spatial Overlay
| pin | gross_acres | calc_area | soil_type | muname | globalid_1 | musym | slope | SHAPE__Length_1 | objectid_1 | ... | created_user | landuse | globalid_2 | landuse_type | last_edited_date | created_date | SHAPE__Length_2 | objectid_2 | SHAPE__Area_2 | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73 | 08-27-100-001 | 160.0199 | 7.089146e+06 | 330 | Peotone silty clay loam, 0 to 2 percent slopes | {B91AB7B3-0048-4DF2-8EA3-3C7E9AF4FAA2} | 330A | A1 | 1.164396e+04 | 5727 | ... | jcarlson | CR | {5BB53B1C-6DE7-4437-80CA-66D27165C57D} | 2 | 1689080298000 | 1689080298000 | 19494.803128 | 2523 | 6.524488e+06 | POLYGON ((962081.614 1755311.678, 962061.878 1... |
| 138 | 08-27-200-001 | 160.0503 | 7.052477e+06 | 235 | Bryce silty clay, 0 to 2 percent slopes | {06C67944-4F22-4A6D-9075-4D765B3CCECC} | 235A | A1 | 1.058461e+06 | 4851 | ... | jcarlson | ROW | {D055454D-64CD-49D2-A11F-3F77D8B37343} | 6 | 1689080298000 | 1689080298000 | 1387.146435 | 71669 | 1.990635e+04 | POLYGON ((964735.912 1755700.543, 964735.912 1... |
2 rows × 22 columns
Remove Extra Fields
keepers = [
'gross_acres',
'gis_acres',
'calc_area',
'pin',
'soil_type',
'slope',
'landuse_type',
'geometry'
]
df.drop(columns=[c for c in df if c not in keepers], inplace=True)
df.sample()| pin | gross_acres | calc_area | soil_type | slope | landuse_type | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 141 | 08-27-400-008 | 158.85 | 6.948153e+06 | 44 | A1 | 6 | POLYGON ((963479.829 1751019.891, 963479.829 1... |
Calculating Part Area
Validate Results
Check Acreage Sums
| pin | gross_acres | part_acres | diff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 08-27-100-001 | 160.0199 | 160.0199 | 0.0 |
| 1 | 08-27-200-001 | 160.0503 | 160.0503 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 08-27-300-002 | 162.5298 | 162.5298 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 08-27-400-007 | 0.1800 | 0.1800 | 0.0 |
| 4 | 08-27-400-008 | 158.8500 | 158.8500 | 0.0 |
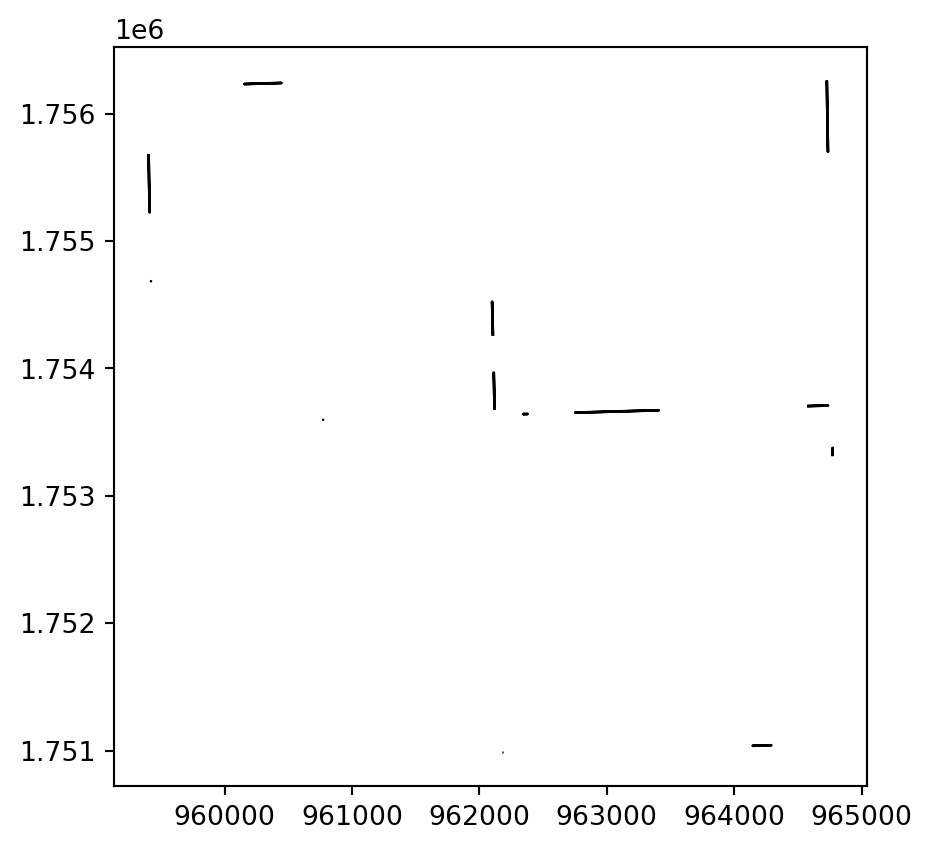
Visualize Gaps
Tidy Up and Export
Fields
| pin | soil_type | slope | landuse_type | part_acres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 0827100001 | 44 | A1 | 02 | 3.629458e-07 |
Agregating
out_cols = ['pin', 'soil_type', 'slope', 'landuse_type']
aggs = {
'soil_type':'first',
'slope':'first',
'landuse_type':'first',
'pin':'first',
'part_acres':'sum'
}
agg_df = df.groupby(by=out_cols, as_index=False).agg(aggs).reset_index(drop=True)
agg_df.head()| soil_type | slope | landuse_type | pin | part_acres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 101 | A1 | 02 | 0827100001 | 0.019314 |
| 1 | 137 | A1 | 02 | 0827100001 | 30.233261 |
| 2 | 137 | B1 | 02 | 0827100001 | 7.898314 |
| 3 | 152 | A1 | 02 | 0827100001 | 30.680595 |
| 4 | 324 | B1 | 02 | 0827100001 | 0.821661 |
Rounding and Filtering
| soil_type | slope | landuse_type | pin | part_acres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 | 235 | A1 | 01 | 0827400008 | 2.485521e-07 |
| 48 | 137 | A1 | 04 | 0827400008 | 2.818391e-06 |
| 61 | 69 | A1 | 04 | 0827400008 | 1.106778e-02 |
| 7 | 44 | A1 | 04 | 0827100001 | 1.594348e-02 |
| 43 | 189 | A1 | 06 | 0827400007 | 1.796944e-02 |
Export to File
0 101 A1 02 0827100001 0.0193
1 137 A1 02 0827100001 30.2333
2 137 B1 02 0827100001 7.8983
3 152 A1 02 0827100001 30.6806
4 324 B1 02 0827100001 0.8217
5 330 A1 02 0827100001 25.2632
6 44 A1 02 0827100001 64.817
7 44 A1 04 0827100001 0.0159
8 69 A1 02 0827100001 0.2706
9 101 A1 02 0827200001 8.4191
10 137 A1 02 0827200001 15.7057
11 137 A1 04 0827200001 0.7579
12 137 B1 02 0827200001 27.1341
13 137 B1 04 0827200001 0.3285
14 152 A1 02 0827200001 12.5491
15 189 A1 01 0827200001 0.0617
16 189 A1 02 0827200001 1.2277
17 189 A1 04 0827200001 3.366
18 235 A1 01 0827200001 0.3729
19 235 A1 02 0827200001 18.0763
20 235 A1 04 0827200001 3.2155
21 235 A1 06 0827200001 1.5946
22 324 B1 02 0827200001 8.5981
23 324 B1 04 0827200001 0.1339
24 325 B1 02 0827200001 7.2118
25 325 B1 04 0827200001 0.3255
26 330 A1 02 0827200001 6.8945
27 67 A1 02 0827200001 22.261
28 67 A1 04 0827200001 0.4837
29 69 A1 02 0827200001 17.9257
30 69 A1 04 0827200001 1.1287
31 91 A1 02 0827200001 2.0659
32 91 A1 06 0827200001 0.2125
33 101 A1 02 0827300002 28.0172
34 137 A1 01 0827300002 1.1427
35 137 A1 02 0827300002 55.2876
36 137 A1 04 0827300002 2.0482
37 137 A1 06 0827300002 1.7998
38 149 A1 02 0827300002 2.4657
39 152 A1 02 0827300002 58.2811
40 152 A1 06 0827300002 0.1124
41 44 A1 02 0827300002 13.3751
42 189 A1 02 0827400007 0.162
43 189 A1 06 0827400007 0.018
44 101 A1 02 0827400008 50.6161
45 101 A1 04 0827400008 0.2853
46 101 A1 06 0827400008 0.3412
47 137 A1 02 0827400008 6.2651
49 137 A1 06 0827400008 1.3067
50 152 A1 02 0827400008 84.5602
51 152 A1 06 0827400008 0.9759
52 189 A1 02 0827400008 2.4665
53 189 A1 04 0827400008 1.0565
54 189 A1 06 0827400008 0.101
56 235 A1 02 0827400008 2.267
57 235 A1 06 0827400008 0.2318
58 44 A1 02 0827400008 4.0168
59 44 A1 06 0827400008 1.1258
60 69 A1 02 0827400008 3.2228
61 69 A1 04 0827400008 0.0111
Valuation
Extra Tables
- Soil Productivity Index Values
- Slope and Erosion Adjustment Coefficients
- Equalized Assessed Value / PI Table
| map_symbol | soil_type | favorability | productivity_index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 596 | 692 | Beasley silt loam | Favorable | 95.0 |
| 719 | 841 | Carmi - Westland complex | Favorable | 99.0 |
| 858 | 977 | Neotoma-Wellston complex | Unfavorable | 74.0 |
| 472 | 556 | High Gap loam | Unfavorable | 84.0 |
| 704 | 824 | Schuline silt loam | Favorable | 82.0 |
Slope and Erosion Coefficients
Our soil data comes with slope / erosion codes with the following ranges:
| Code | %Slope |
|---|---|
| None / A | 00 - 02 |
| B | 02 - 05 |
| C | 05 - 10 |
| D | 10 - 15 |
| E | 15 - 18 |
| F | 18 - 35 |
| G | 35 - 70 |
Per Pub 122:
Because Table 3 cannot be used with slope ranges, use a central point of the slope ranges unless a better determinant of slope is available.
EAV
Table 1 in Pub 122 gives us the per-acre EAV for a given PI.
However! There is a minimum certified PI.
To calculate values below that minimum, IDOR provides the following calculations, and we take whichever is greater.
\[ EAV^{PI_{n}} = EAV^{PI_{min}} - \left(\frac{EAV^{PI_{min+5}} - EAV^{PI_{min}}}{5} * (min - n)\right) \]
\[ EAV^{PI_{n}} = \frac{EAV^{PI_{min}}}{3} \]
Floor: 66.43| avg_PI | eav | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 66.774 |
| 1 | 2 | 68.410 |
| 2 | 3 | 70.046 |
Merge DataFrames
val_df = agg_df.merge(pi_df, how='left', left_on='soil_type', right_on='map_symbol', suffixes=('','_desc'))
val_df = val_df.merge(se_df, how='left', left_on='slope', right_on='erosion_code')
val_df.sample(2)| soil_type | slope | landuse_type | pin | part_acres | map_symbol | soil_type_desc | favorability | productivity_index | erosion_code | slope_desc | eros_desc | coeff_fav | coeff_unf | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | 137 | A1 | 06 | 0827400008 | 1.3067 | 137 | Clare silt loam, bedrock substratum | Favorable | 113.0 | A1 | 0-2% | UNERODED | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 30 | 69 | A1 | 04 | 0827200001 | 1.1287 | 69 | Milford silty clay loam | Favorable | 113.0 | A1 | 0-2% | UNERODED | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Adjusted PI
val_df.insert(
5,
'adj_PI',
np.where(
val_df['favorability'] == 'Favorable',
val_df['productivity_index'] * val_df['coeff_fav'],
val_df['productivity_index'] * val_df['coeff_unf']
)
)
val_df[['productivity_index', 'favorability', 'adj_PI']].sample(3)| productivity_index | favorability | adj_PI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | 113.0 | Favorable | 113.0 |
| 54 | 107.0 | Favorable | 107.0 |
| 15 | 115.0 | Favorable | 115.0 |
Merge in EAVs
Landuse Adjustments
| Landuse | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Cropland | \(EAV\) |
| Permanent Pasture | \(\frac{EAV}{3}\) |
| Other Farmland | \(\frac{EAV}{6}\) |
| Contributory Wasteland | \(33.22\) |
val_df.insert(6, 'eav_adj', 0)
val_df.loc[val_df['landuse_type'] == '02', 'eav_adj'] = val_df['eav']
val_df.loc[val_df['landuse_type'] == '03', 'eav_adj'] = val_df['eav']/3
val_df.loc[val_df['landuse_type'] == '04', 'eav_adj'] = val_df['eav']/6
val_df.loc[val_df['landuse_type'] == '05', 'eav_adj'] = 33.22
val_df[['landuse_type', 'eav', 'eav_adj']].sample(5)| landuse_type | eav | eav_adj | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 02 | 426.08 | 426.08 |
| 32 | 06 | 369.43 | 0.00 |
| 27 | 02 | 491.66 | 491.66 |
| 2 | 02 | 436.56 | 436.56 |
| 42 | 02 | 469.07 | 469.07 |
Multiply EAV by Acres
val_df['value'] = val_df['part_acres'] * val_df['eav_adj']
val_df[['pin', 'soil_type', 'slope', 'landuse_type', 'part_acres', 'value']].fillna(0).sample(5)| pin | soil_type | slope | landuse_type | part_acres | value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49 | 0827400008 | 152 | A1 | 02 | 84.5602 | 68256.147838 |
| 52 | 0827400008 | 189 | A1 | 04 | 1.0565 | 82.595409 |
| 10 | 0827200001 | 137 | A1 | 02 | 15.7057 | 7023.903154 |
| 28 | 0827200001 | 67 | A1 | 04 | 0.4837 | 39.635990 |
| 0 | 0827100001 | 101 | A1 | 02 | 0.0193 | 8.223344 |
Per-Parcel Totals
| part_acres | value | |
|---|---|---|
| pin | ||
| 0827100001 | 160.0199 | 73548.277557 |
| 0827200001 | 160.0504 | 68556.261183 |
| 0827300002 | 162.5298 | 89997.880404 |
| 0827400007 | 0.1800 | 75.989340 |
| 0827400008 | 158.8498 | 97539.361467 |
And how does this compare?
| PIN | Mine | Theirs |
|---|---|---|
| 0827100001 | 73,548.28 | 73,550.00 |
| 0827200001 | 68,556.26 | 68,550.00 |
| 0827300002 | 89,997.88 | 90,000.00 |
| 0827400005 | 52,400.21 | 52,400.00 |
| 0827400006 | 45,154.87 | 45,150.00 |
| 0827400007 | 75.99 | 80.00 |
Taking Things Further
- Standalone function that takes lists / input files of parcel numbers
- Wrap process in a GUI for other staff
- Put function into cloud environment, trigger via API?
- Generate per-parcel PDFs w/ maps, tables
Questions?